- Published on: 7 Oct 2025
- Last updated on: 7 Oct 2025
- Post Views: 24701


If you’re moving goods in India from one location to another, you need to record and document the transportation legally. This allows businesses and the government to trace transactions and prevent tax evasion. To fulfil this purpose, the government of India introduced the E-Way Bill (EWB). This system ensures that all consignments of goods with a specific value or distance are legal and traceable. In this blog, we’ll understand what an E-Way Bill is, its rules, limits and generation process.

An Electronic Way Bill or E-Way Bill is an electronically generated bill that facilitates the movement of goods from one place to another. It contains all the details of the consignment, like invoice number, date, value of the goods, vehicle number, and details of the transporter.
The government of India rolled out the system on April 1, 2018 and mandated every business to generate an E-Way Bill online for the transportation of goods of over ₹50,000. It improves how the products are transferred, tracked and accounted for. A special E-Way Bill Number (EBN) is allocated when the bill is generated.
Also read: GST Registration Process.
| Part A (Invoice-related information) | Invoice number and date Supplier and recipient’s GST (Goods and Services Tax) registration numbers Description and value of goods PIN code of the place of dispatch and delivery |
| Part B (Vehicle-related details) | Mode of transport (road, air, rail, or ship) Vehicle number Document number and date of transport |

An E-Way Bill must be generated by the individual who is responsible for the transportation of goods. This person can be the consignor (the owner and sender of goods) or consignee (the party who receives the goods). Here is when you must generate an E-Way Bill:
In some cases, E-Way Bills must be issued even if the value is below ₹50,000. For instance:
According to the E-Way Bill rules, the document is valid for a certain period only. This is based on the distance that has to be traversed by the products:
| Type of Conveyance | Distance | Validity |
| Standard Goods | Less than 200 km | 1 day |
| 200 km and above | 1 day for every 200 km or portion thereof | |
| Over-Dimensional Cargo | Less than 20 km | 1 day |
| 20 km and above | 1 extra day per 20 km or portion thereof |
For instance, if you want the truck to transport goods for 500 km, the bill should be for 3 days (200 km = 1 day, next 200 km = 1 day, remaining 100 km = 1 day).
Also read: GST-Based Loans.

The key requirement for generating the E-Way Bill is that the individual must be registered on the GST portal and the E-Way Bill portal. If you meet these prerequisites, follow these steps to generate an E-Way Bill:
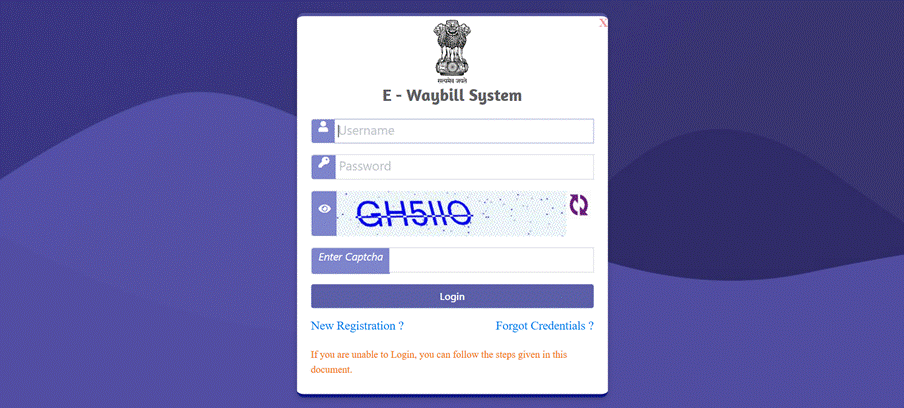
Step 1: Log in to EWB Portal
Visit the official E-Way Bill portal for seamless eWay bill login. Enter your username (ID), password, and captcha code, and then press the Login button.
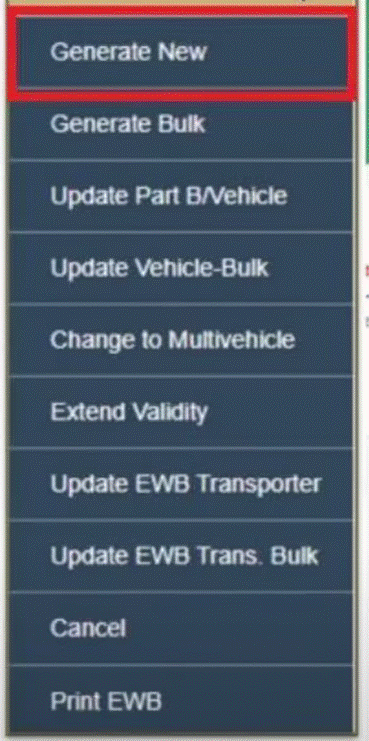
Step 2: Select “Generate New”
Click on the ‘Generate New’ button situated on the upper left-hand side of the menu in the dashboard.
Step 3: Enter the Transaction Details:
You will see a form now that you have to fill out with the consignment details.

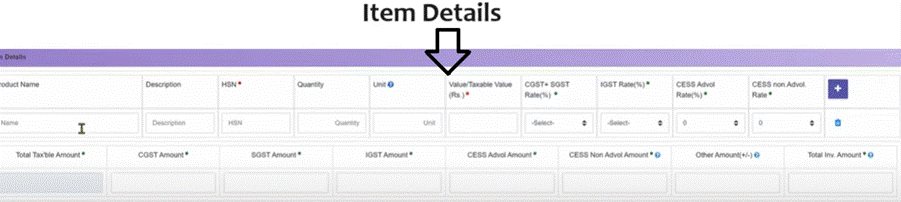
Step 4: Enter Item Details
Here you must provide product-specific information like:
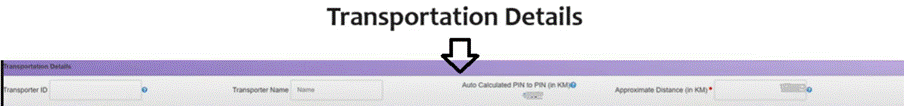
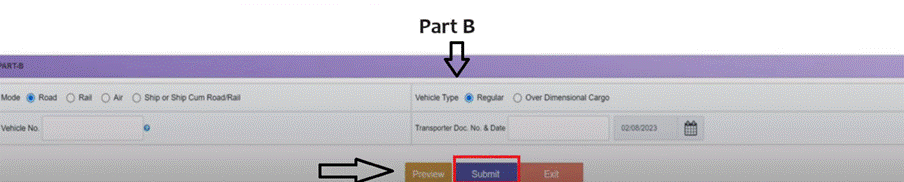
Step 5: Enter Transporter Details
Specify how the goods will be transported. Mention the mode of transport (road, rail, air, or sea) and the approximate distance in kilometres. You also need to furnish either:
Step 6: Submit the Form
After all the details have been filled out, click Submit. The system will check your details. If everything is good, the system will automatically generate the E-Way Bill (Form EWB-01) bearing a distinct 12-digit E-Way Bill Number (EBN).
Step 7: Download and Print the Form
After you receive the 12-digit EBN, go to the bottom of the page and click the Print button to print the document.
The E-Way Bill rules provide exceptions under which an E-Way Bill is not needed.
Noncompliance with GST transport compliance can result in severe fines. Here are the penalties that a E-Way Bill noncompliance can attract:

The E-Way Bill system is a mandatory component of GST compliance. It brings transparency, legality, and ease to the movement of goods. This is why every business should know the GST E-Way Bill limit and rules to ensure that they’re compliant and won’t have to face legal scrutiny or penalties. It also acts as proof of legal business operations and GST compliance, which can improve the approval chances of getting a business loan. If you want to apply for a business loan, click here.
1. What is the minimum value for which an E-Way Bill is required?
An E-Way bill is required when the value of goods exceeds ₹50,000 in a single invoice or when multiple consignments in one vehicle cross this amount.
2. Can I generate an E-Way bill without GST registration?
No, the government of India mandates having a valid GST Identification Number (GSTIN) to generate an E-Way Bill.
3. Can an E-Way Bill be generated through SMS?
Yes, after registering your mobile number on the portal, you can use SMS codes to generate or cancel E-Way Bills.
4. What happens if the E-Way Bill expires during transit?
You can extend the validity period either 8 hours before or after the expiry, provided the goods are still in transit.
5. Is an E-Way Bill required for the movement of goods below ₹50,000?
Not usually, but in certain special cases, like interstate job work or handicraft goods movement, it is required.
6. Can multiple consignments be covered under one E-Way Bill?
Yes, you can generate a consolidated E-Way Bill using the EWB-02 form if multiple consignments are carried in one vehicle.
7. Do I need to carry a physical copy of the E-Way Bill?
Not necessarily. A digital copy of the EBN number is enough for authorities to verify.
8. Who is responsible for generating the E-Way Bill, the supplier or transporter?
Both the supplier (consignor) and the recipient (consignee) are primarily responsible for generating the E-way Bill.
9. Is filling in transport details always required?
No. If the distance between the consignor and transporter is less than 50 km, you don’t need to provide full transport details.
10. What is the penalty for not generating an E-Way Bill?
The penalty is ₹10,000 or the tax evaded amount, whichever is higher. Goods and the vehicle may also be seized.


