- Published on: 18 Nov 2025
- Last updated on: 27 Jan 2026
- Post Views: 7845


The active taxpayer registration in India surpassed 1.51 crore in 2025. The Goods and Services Tax (GST) scheme mandates that many of the regular taxpayers file GST invoices, except those under the Composition Scheme and NIL-rated. It is a legal document that states what you sold, who bought it, and at what price. The GST invoice format ensures that it provides all the information about the sale.
To ensure your business complies with the GST invoicing rules and customers can claim input tax credits (ITC), you must create a GST invoice that contains all the mandatory details. In this blog, we will understand everything about GST invoicing rules and format.

A GST Invoice (or GST bill) is a formal document that shows the products or services sold, their quantity, their price, and the tax amount charged. It serves as evidence of the transaction that is used by both the buyer and the seller to remain compliant with the GST law.
It is mandatory for GST-registered businesses and regular taxpayers to issue an invoice every time goods or services are provided. It allows buyers to claim ITC and shows that all the taxable supplies have been properly accounted for.
Rule 46 of the CGST Rules, 2017 mandates businesses to provide specific details in the GST invoice. If your invoice is missing even one of them, it can be considered invalid. Here is what a GST invoice must look like when you are billing your customer:
In case the recipient is not registered and the invoice value is more than ₹50,000, it is also necessary to provide:

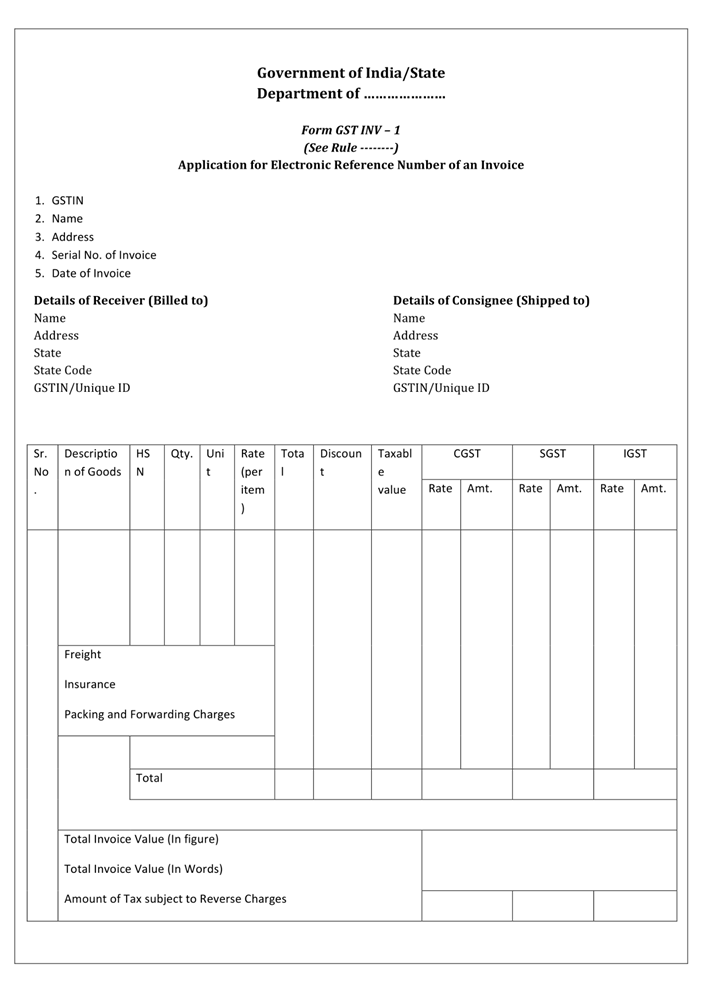
Here is a GST invoice sample you can use as an example to understand the structure and format. You can also download the GST bill format PDF for billing:
Different types of businesses need to issue different types of invoices under GST invoicing rules. Here are the primary types of GST invoices:
1. Tax Invoice
A tax invoice is generated when a GST-registered business sells taxable goods or provides taxable services. The document contains all the tax details, ranging from suppliers’ and recipients’ information to HSN and SAC codes. It allows the buyer to claim input credits.
2. Bill of Supply
The bill of supply carries a close resemblance to the GST invoice in every aspect except that it does not incorporate the details of tax, and the seller does not levy taxes. It is issued in cases where the seller cannot charge GST, such as:
3. Invoice-cum-Bill of Supply
If a business is selling both taxable and exempt goods or services to an unregistered customer, it issues invoice-cum-bill of supply. This lets the business prevent confusion and duplication of documents.
4. Aggregate Invoice
A business issues an aggregate invoice when there are multiple minor sales to unregistered customers within a day, and every invoice amounts to less than ₹200. The aggregate invoice covers all those transactions for that day.
5. Revised Invoice
A business is required to get its GST registration right after the issuance of the invoices. In this case, it has to issue a revised invoice for the transactions that take place earlier within a month from the date of registration.

Here are the mandatory GST invoice requirements that a business must meet to issue a GST invoice:
Here are the important GST invoice rules that every business must know and follow:
The CGST Act lays down the timing and rules for issuing invoices. Failure to meet these GST deadlines may lead to compliance or tax problems. Here’s the general timeline:
| Type of Supply | Time Limit for Issuing Invoice |
| Goods (Normal Case) | On or before the date of removal or delivery |
| Goods (Continuous Supply) | On or before the date of issue of the account statement or payment |
| Services (General Case) | Within 30 days of providing the service |
| Services (Banks/NBFCs) | Within 45 days of providing the service |
An invoice issued without a valid IRN or QR code is considered a non-issuance of an invoice and is subject to penalties under Section 122 of the CGST Act, and the buyer may not receive the Input Tax Credit.
Every invoice must be identified by a unique consecutive serial number, which can be up to 16 characters long, and can contain letters, numbers, as well as special characters such as “/” or “-“, etc. This rule exists to ensure that there will be no duplicate invoice numbers in a particular financial year.
The rules above serve the purpose of tracking in a clearer way, and at the same time, they act as safeguards against duplication or misuse.

Here are some common mistakes you must avoid and tips to ensure compliance:
A GST invoice serves as an important compliance tool that facilitates financial transparency, accurate tax collection, and input tax credits. Businesses must comply with the rules and follow the correct GST invoice format. The key benefit of this is that it helps you maintain proper GST records. When you apply for a business loan, it serves as income proof and improves your chances of approval.
1. Can I issue a GST invoice without HSN or SAC codes?
No, you cannot issue a GST invoice without HSN/SAC codes, as you are mandated to provide them in your invoice.
2. What happens if I cancel a GST invoice after issuing it?
If you cancel a GST invoice after issuing it, you must issue a credit note to nullify the earlier invoice.
3. Is it mandatory to issue a GST invoice for advance payments?
Yes, you must issue a receipt voucher for every advance received, showing the amount and applicable tax rate.
4. Can a single invoice cover multiple GST rates?
Yes, you can include multiple GST rates in one invoice, but you must show tax calculations separately for each rate.
5. Do I need separate invoices for interstate and intrastate sales?
No, you don’t need separate invoices for interstate and intrastate sales. One sales invoice is sufficient, but ensure that the place of supply and GST type are correctly mentioned.
6. Can I issue invoices in a foreign currency?
Yes. You can issue invoices in foreign currency, but you will also have to indicate the taxable value in Indian Rupees (INR) as per the exchange rates on the date of the invoice.
7. What if I make a typing error in an e-invoice?
In case of an error in an E-Invoice, cancel it within 24 hours on the IRP (Invoice Registration Portal) and re-issue a new corrected invoice.
8. Are handwritten GST invoices allowed?
Yes. The invoices written by hand are legally accepted, but digital invoices are suggested to be more accurate, store, and integrated with e-invoicing.
9. Can I use the same invoice number format every year?
Yes. You can use the same invoice numbering system every year, but you need to resume numbering with every financial year.
10. Do I need a GST invoice for zero-rated exports?
Yes. Exporting requires a GST invoice, which is used as evidence of supply, and you can claim export refunds or input tax credits.


